Manual cash application is the silent killer of finance productivity. According to industry data, mid-market finance teams spend between 40–60 hours every month just reconciling payments with invoices.
As we enter 2026, the shift from manual data entry to AI-driven straight-through processing is no longer optional if you want to scale without burning out your team.
This guide walks you through:
-
Definition: What cash application automation is (in plain English).
-
Why now: Why it matters in 2026, specifically.
-
Roadmap: A step-by-step implementation plan you can run in weeks, not quarters.
-
Vendor criteria: The key features to demand from any vendor.
What is Cash Application Automation?

Cash application automation is the use of software, increasingly powered by AI and machine learning, to match customer payments to open invoices in your accounts receivable (AR) ledger and post the results automatically.
In normal life, it looks like this:
-
Payment Arrival: A payment hits your bank account.
-
Data Capture: Remittance advice shows up somewhere messy (email, PDF, portal download, lockbox file).
-
Ledger Matching: The system links payment → customer → invoice(s) and posts it to your accounting system.
Older tools relied on rigid rules. That breaks the second a customer forgets an invoice number or changes their remittance template. Modern systems use confidence-based matching, which means the tool makes a best match and assigns a confidence score (for example, 98% match).
The end goal is straight-through processing (STP), where transactions flow from start to finish without human touch. If you want a simple definition, Wikipedia’s overview is a good starting point: Straight-through processing (STP).
Why Automate Cash Application in 2026?
Payment friction is rising, not falling. Recent trends show that 45% of CFOs have faced payment disruptions due to invoicing errors that could have been prevented with automation.
Here is what you get when you stop living in spreadsheets.
Key Benefits Include
-
Reduced Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): Faster posting means you see what is actually overdue, faster. That helps you act earlier, protect cash flow, and free credit limits. For a clean definition of DSO and why it impacts cash, see the Association for Financial Professionals (AFP).
-
Higher Accuracy: You remove copy-paste errors, missed discounts, and “fat-finger” postings that create avoidable disputes.
-
Staff Empowerment: Your AR team can shift from data entry to higher-value work like exception analysis, customer follow-up, and better forecasting. If you are building a more strategic finance function, this pairs well with strategic financial planning.
-
Real-time Visibility: Cash position becomes a live dashboard, not a Friday report. That changes how confidently you can spend, hire, and invest.
How to Implement Cash Application Automation: Step-by-Step
The fastest implementations follow a simple rule: start by centralizing the “noise”, then automate matching, then tighten exception workflows. Do not try to perfect everything on day one.
Step 1: Centralize Payment and Remittance Data
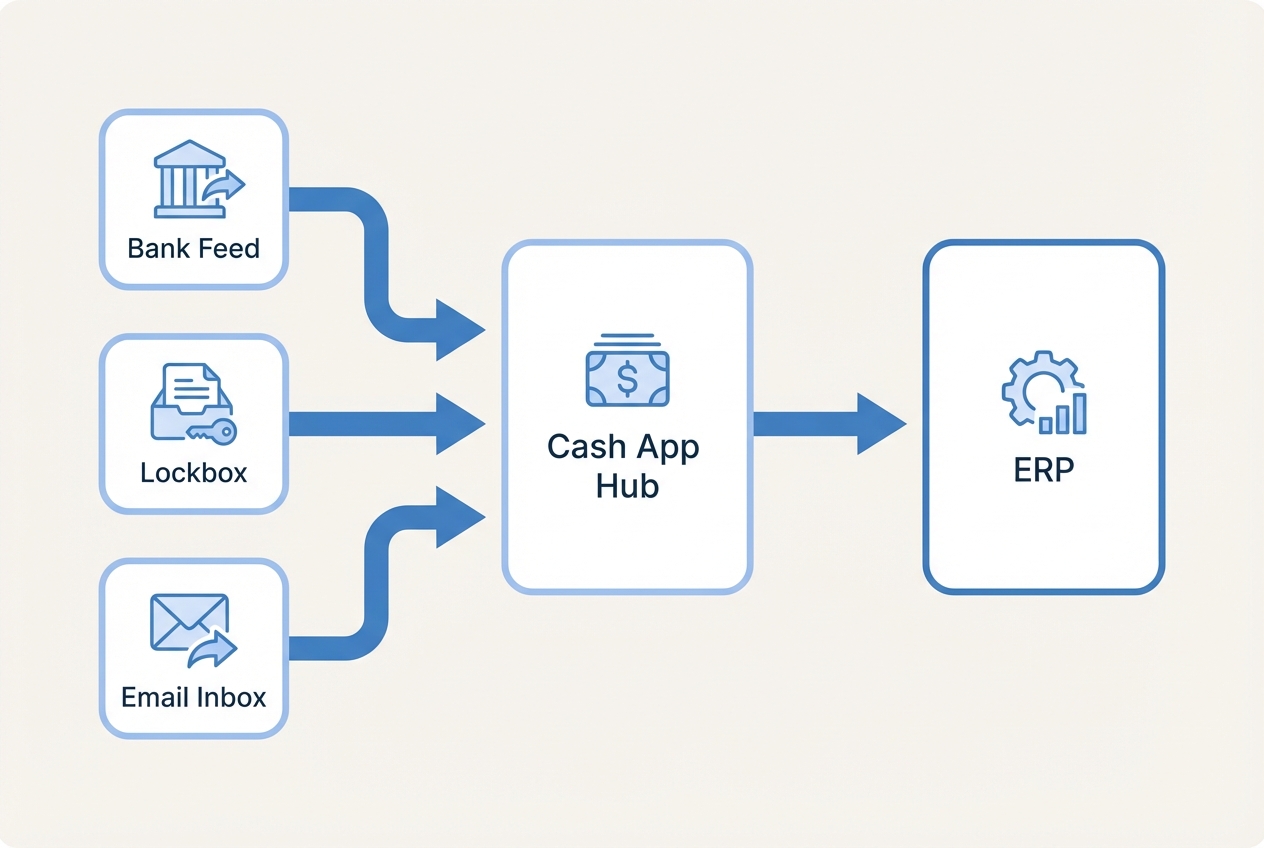
Automation starts with aggregation. You must connect to every place payments and remittance info appear, including:
-
Bank Files: Connect to formats like BAI2 and MT940 so you have a clean, reliable record of cash-in.
-
Lockbox Files: Pull check payment data your bank processes, including any remittance details the lockbox captures.
-
Remittance Inboxes: Connect shared email inboxes where customers send remittance advice as PDFs, spreadsheets, or message text.
-
Customer Portals: Capture portal remittances where someone on your team currently logs in weekly to download PDFs.
Why this matters: if remittance is scattered, your automation tool is blind. It cannot match what it cannot see.
Implementation notes (keep it simple):
-
Start with the Bank Feed: This is your source of truth for what cash actually arrived.
-
Add Remittance Channels Next: Email and lockbox are usually the highest ROI.
-
Document Each Source: Who owns it, where it lives, how often it updates, and what file types show up.
If your team is dealing with bank reporting formats, you may run into BAI2. Here is a plain-English explainer you can share internally: What is BAI2?
Step 2: Leverage AI for Data Extraction
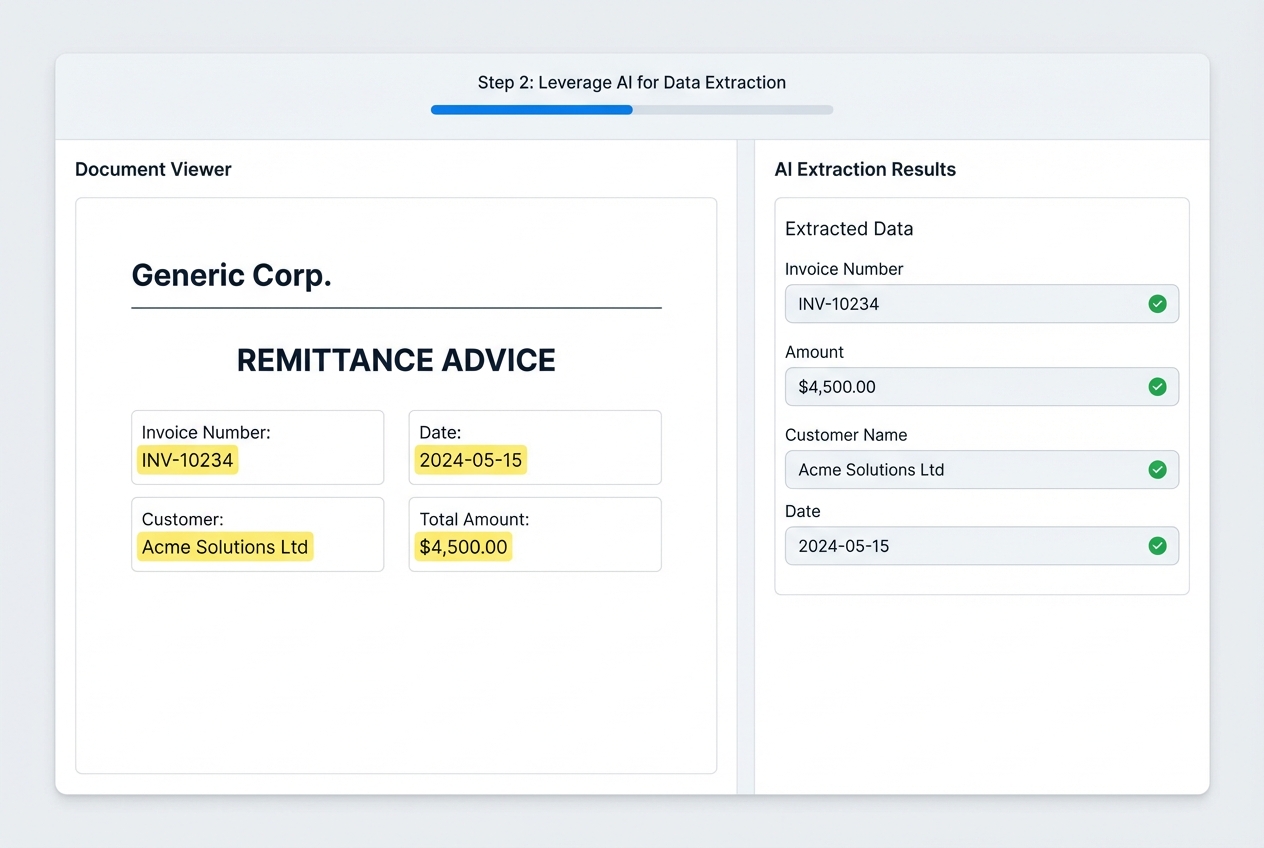
This is where a lot of “automation projects” die. Traditional OCR (optical character recognition) reads characters, but it does not reliably understand context. Remittance advice is messy by nature. People email screenshots, send PDFs with weird tables, or paste invoice lists into email bodies.
What you actually want is intelligent document processing (IDP). IDP uses OCR plus AI to understand structure and extract fields with validation logic. TechTarget’s definition is a solid overview: Intelligent document processing (IDP).
What to configure in this step:
-
Invoice Identifiers: Invoice number, PO number, account number (whatever your customers actually include).
-
Amounts: Paid amount, discount taken, short pay amount.
-
Dates: Payment date, invoice dates (helps disambiguate duplicates).
-
Customer Mapping: Link remittance to the right customer record even when names are inconsistent.
In 2026, if your vendor only offers “OCR templates,” you will spend too much time maintaining rules. You want learning-based extraction so the system adapts as formats change.
Step 3: Execute Intelligent Invoice Matching
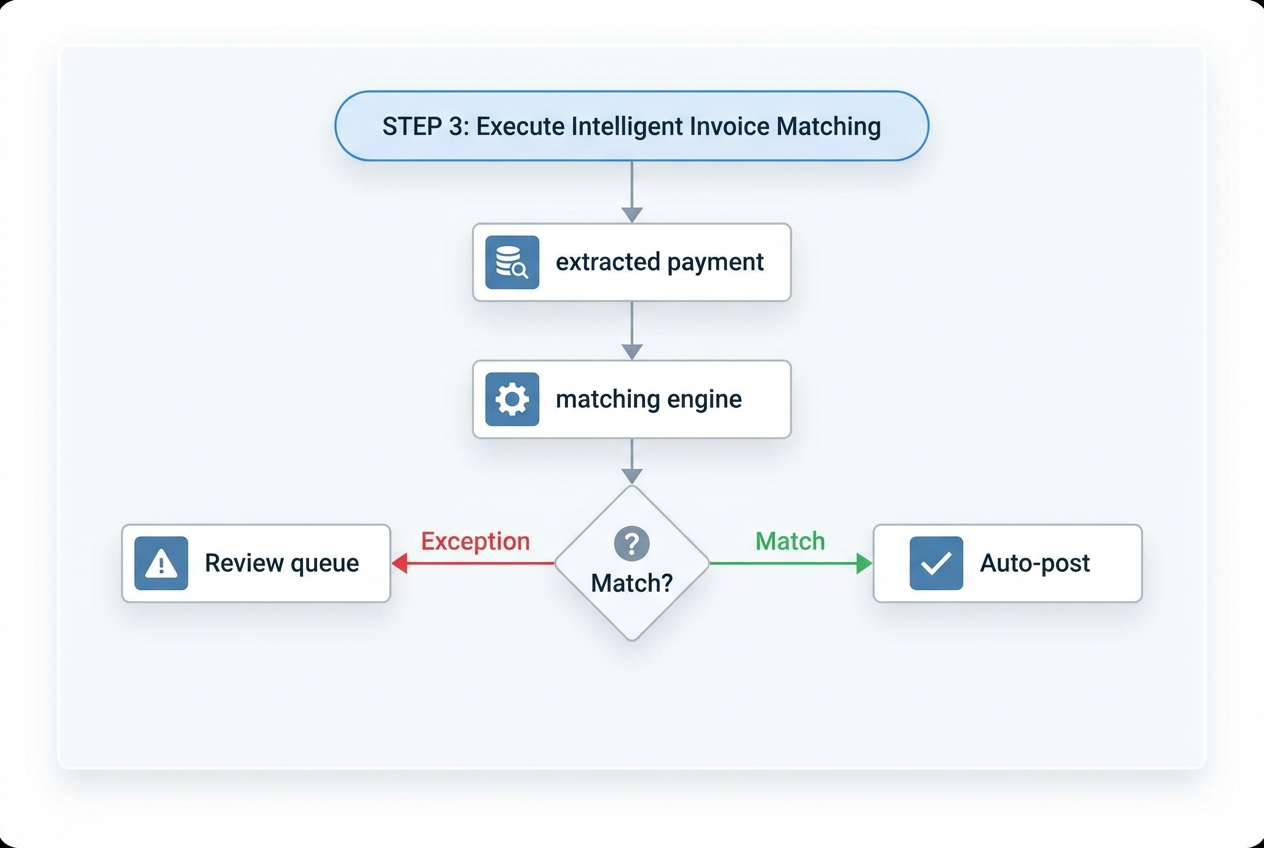
Once you have structured payment and remittance data, your matching engine compares it against open invoices in your AR.
This is where modern cash application automation goes beyond “invoice number equals invoice number.”
It should handle real-world cases like:
-
Consolidated Payments: One payment covering multiple invoices.
-
Short Pays and Deductions: Including partial invoice payments that require reason codes or workflows.
-
Discounts Taken: Early pay terms, negotiated credits, or consistent “always-takes-2%” behaviors.
-
Parent-child Hierarchies: A parent entity pays for several sub-entities or locations.
-
Duplicate Invoice Numbers: Common across business units, especially after acquisitions.
A practical way to design matching logic:
-
High Confidence (Auto-post): The system posts automatically (for example, ≥ 95% confidence).
-
Medium Confidence (Suggest): A human reviews and confirms in one click.
-
Low Confidence (Investigate): The system flags missing remittance, unclear customer, or potential fraud risk.
Step 4: Automate Exception Handling
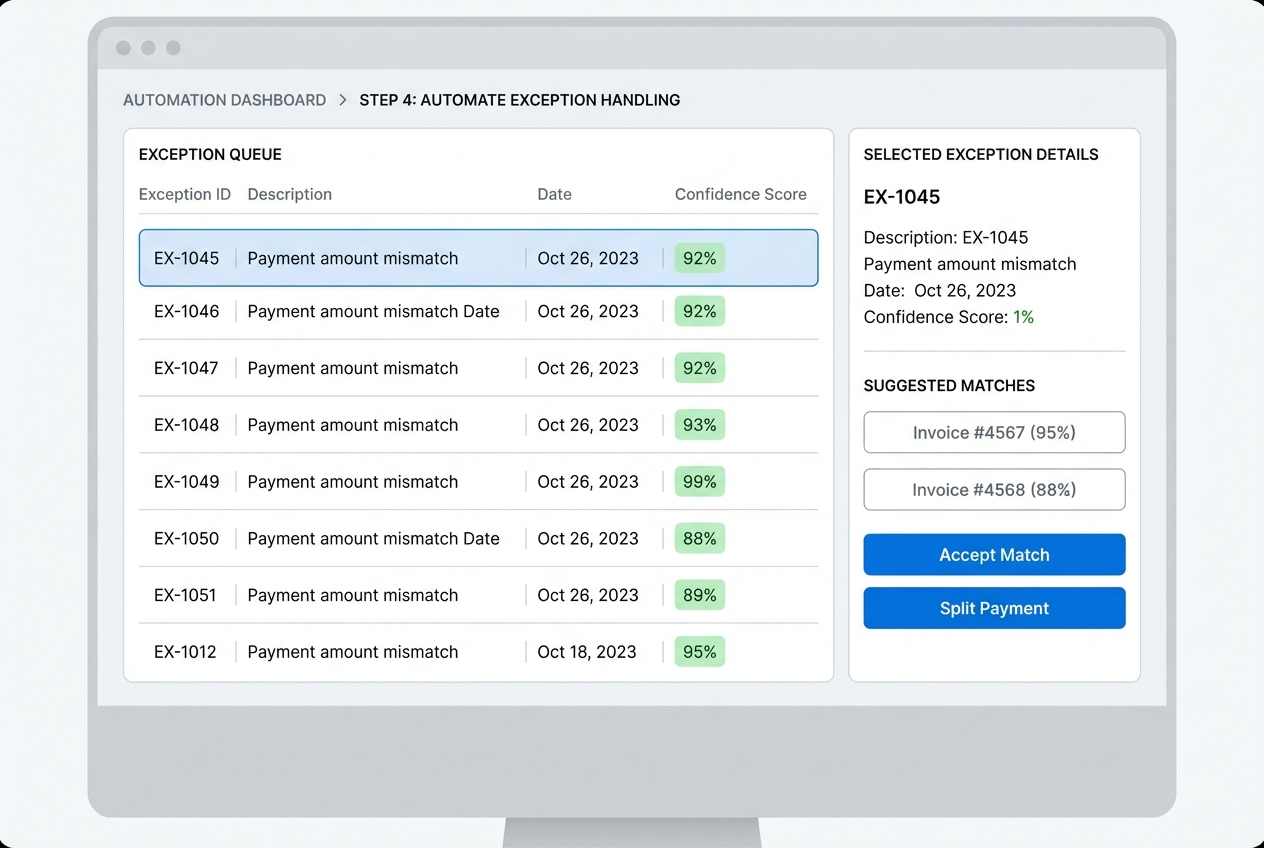
No system hits 100% automation on day one. The win is making exceptions fast, visible, and teachable.
Your goal here is to build a simple exception workflow that:
- Groups exceptions by root cause (missing invoice number, short pay, unknown payer).
- Shows the best suggested matches.
- Lets your team resolve in one click.
- Feeds those corrections back into the model so the exception rate drops over time.
Make exceptions work for you:
-
Create Reason Codes: This helps you spot patterns, like one customer constantly short-paying for freight.
-
Set an SLA: For example, exceptions must be resolved within 48 hours so your AR stays current.
-
Track Learning: Your exception rate should drop month over month as the system learns how your team resolves edge cases.
This is also where small businesses can build a real advantage. When your cash posting is clean, you can run better follow-ups and improve your broader financial operations without hiring a bigger team.
Step 5: Post-Directly to Your ERP
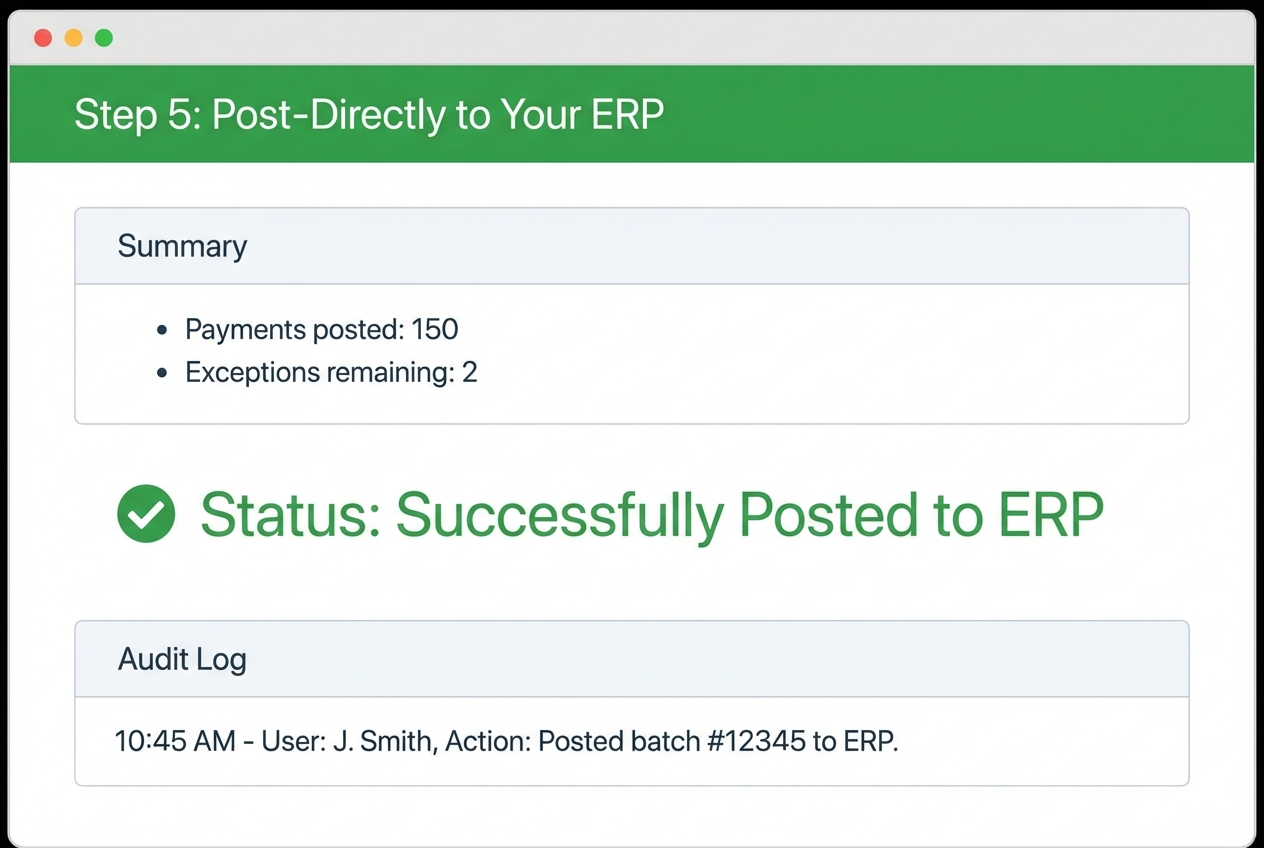
ERP means “Enterprise Resource Planning,” which is a fancy way of saying your core accounting system (NetSuite, SAP, Oracle, QuickBooks Enterprise, and others).
Posting is where automation becomes real. If your tool matches payments but still requires manual entry into the ERP, you are only halfway there.
Your software should:
-
Create and Apply Receipts: Create cash receipts and apply them to invoices automatically so your ledger stays clean.
-
Write Back Reliably: Write back to the ERP in real time (or on a schedule you control) to prevent stale reporting.
-
Maintain Audit Trails: Keep a clear record of what happened, when, and why (critical for controls).
-
Support Corrections: Allow rollbacks or adjustments without breaking the ledger or forcing spreadsheet workarounds.
If ERP integration feels like the scary part, you are not alone. It is also where custom work sometimes becomes necessary, especially with older systems or complex subsidiaries. That is exactly the kind of gap a build-and-support model can cover.
For example, if you want to prototype a lightweight cash app console quickly, then connect it to your ERP later, Quantum Byte’s approach can work well: use the AI app builder to get a working internal tool fast, then bring in the in-house dev team when you need deeper ERP integrations or edge-case handling.
Critical Features of Cash Application Automation Software
When you evaluate vendors (including QuantumByte), focus on capabilities that reduce long-term effort, not just “day one” demos.
Non-negotiables:
-
Adaptive Intelligence: Does it learn from human corrections, or do you maintain rules forever?
-
Multi-channel Capture: Can it pull remittance details from email bodies, PDFs, and portals?
-
Deduction Management: Can it tag and route short pays with reason codes and workflows?
-
ERP Agnostic: Will it still work if you change accounting systems in three years?
Here is a quick comparison you can use in vendor calls:
| Capability | Rule-based automation | AI-driven automation |
|---|---|---|
| Setup time | Faster initial setup, slower long-term | Slightly longer setup, improves over time |
| Handling messy remittance | Fragile when formats change | Adapts to new layouts and patterns |
| Exception rate over time | Often flat | Should decrease as the model learns |
| Ongoing maintenance | High (rule updates) | Lower (review and training loops) |
If you are a small team, another “feature” matters: how fast you can get a working system into production. That is why many founders build a tailored workflow app instead of buying a rigid tool.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Most implementations fail for predictable reasons. The good news: you can plan around them.
-
Data Silos: Involve IT early and get API access (API means a secure way for systems to talk to each other). You need bank feeds, ERP data, and inbox access to live in one workflow.
-
Complex Hierarchies: If you have “ship-to vs bill-to” confusion, insist on confidence-based matching that can use multiple identifiers, not just invoice number.
-
Change Management: Tell your AR team the truth. Automation is there to remove repetitive work, not their judgment. Your best people will become exception managers and process owners, which is a stronger career path than “spreadsheet operator.”
Also, do not underestimate the hidden time sink: moving data between systems. If you are still exporting and importing files, you will keep bleeding hours. This is why ERP write-back and clean integrations matter, and why manual data migration is often the first thing to eliminate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between cash collection and cash application?
Cash collection is getting the customer to pay. Cash application is recording that payment against the correct invoice in your books.
They are connected, but not the same. If cash is not applied quickly, collections teams chase the wrong invoices, customer conversations get messy, and DSO stays higher than it needs to be.
In practice, a tailored internal tool, which can be built quickly and efficiently with Quantum Byte, can bridge the gap by showing collections a real-time view of what is paid, partially paid, or unclear.
Can cash application automation integrate with multiple ERPs?
Yes. Many modern solutions support multiple ERPs at once, which matters if you have subsidiaries, separate business units, or you are in the middle of M&A.
The key question is not “can it connect?” It is “can it keep mappings clean across entities” (customers, invoice numbering, currencies, and subsidiaries).
How does AI improve payment matching accuracy?
AI improves accuracy by recognizing patterns and historical behavior rather than relying on rigid rules.
Example: if a customer always rounds down or always takes the same discount, the system can learn that pattern and suggest the correct match. Over time, your exception queue shrinks because the model learns from the way your team resolves edge cases.
What types of payments does automation support?
Most solutions support:
-
ACH Payments: Electronic transfers via the automated clearing house, usually with addenda or limited payer detail.
-
Wire Transfers: Bank-to-bank transfers that often arrive with minimal remittance context, so matching relies more on behavior and history.
-
Checks via Lockbox: Physical checks processed by your bank, often paired with scanned remittance documents.
-
Credit Card Payments: Card transactions (when relevant for your business), sometimes with processor reports that need normalization.
The hard part is rarely “payment type.” The hard part is remittance quality and how cleanly you can link payer → customer → invoice.
How quickly can we see results from automation?
Most businesses see a clear drop in manual workload within the first 30 days, especially if they start with the highest-volume payment channels.
A realistic expectation looks like:
-
Weeks 1–2: Data sources connected, extraction configured.
-
Weeks 3–4: Matching logic tuned, exception workflow live.
-
Month 2+: Exception rate drops as the system learns.
