Manual bank reconciliation is a notorious bottleneck for finance teams, often consuming dozens of hours every month as transaction volume grows. It is not only tedious. It is risky.
A missed fee can snowball into reporting errors. A duplicate entry can do the same. Timing mismatches can trigger awkward month-end surprises. Then you lose hours chasing down “what happened.” NetSuite highlights how automation can remove much of this effort and make reconciliation faster and more reliable.
In this guide, you’ll learn the mechanics of bank reconciliation automation, from connecting secure data feeds to using AI-powered matching logic. We’ll walk step-by-step through implementation, the features that matter most, and a clean way to handle exceptions without turning your process into a mess.
What is Bank Reconciliation Automation?
Bank reconciliation automation is the process of using software to automatically compare your bank transactions (what the bank says happened) against your internal accounting records (what your books say happened).
Instead of manually importing CSV files and matching line-by-line, automation:
-
Pulls bank activity: Brings transactions in through direct feeds, so your data arrives without manual exports.
-
Standardizes fields: Normalizes dates, amounts, currencies, and descriptions so matching rules behave consistently.
-
Matches records: Links bank lines to invoices, payouts, deposits, and journal entries with rules and AI.
-
Creates an audit trail: Logs what happened, when it happened, and why a match was made.
The big shift is from periodic reconciliation (once a month, under pressure) to continuous reconciliation (daily, or even near real-time). That means fewer surprises and faster decisions.
This is also where process automation becomes a real business advantage. When you remove manual entry and repetitive checking, you reduce both cost and chaos. If you’re building broader “close the books” workflows, bank rec automation fits naturally into a bigger automation strategy like process automation.
Matching is only the start. The bigger win is data integrity. When your bank and General Ledger (GL) stay aligned, your cash position becomes something you can trust, not something you hope is correct.
The Core Benefits of Automating Bank Reconciliation
-
Error reduction: Automation reduces the human error factor that causes mismatches, mis-postings, and missing items. SKsoft highlights how reconciliation and settlement automation improves accuracy and reduces discrepancies
-
Time savings: Many teams see reconciliation time drop dramatically (often up to ~80%) because matching, grouping, and coding runs automatically. Your team stops spending nights and weekends on “closing tasks.”
-
Enhanced fraud detection: Real-time matching helps you spot unauthorized transactions faster. The sooner you see an unknown wire or an odd vendor name, the easier it is to act.
-
Scalability: Automation lets a lean finance team handle 10x transaction volume without adding headcount. That is huge when your business grows faster than your back office.
How to Implement Bank Reconciliation Automation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Connecting Direct Bank Feeds
Goal: Stop relying on CSV exports and manual imports. Start with direct feeds.
When you connect directly, your reconciliation system receives bank transactions automatically. This is what makes continuous reconciliation possible.
What to do:
- Feed method: Choose your connection path (direct bank API, Open Banking provider, or your ERP’s banking connector).
- Security controls: Confirm security requirements. Use read-only access where possible. Apply least-privilege permissions and strong authentication.
- Refresh schedule: Set your refresh frequency. Daily is a great start. Move toward near real-time if you need faster visibility.
Security note: if you are using Open Banking style connections, follow a standard security profile (like FAPI-based guidance) to reduce risk.
If your feeds are messy or scattered across banks, start by automating intake first. General process automation is an important first step.
Step 2: Mapping Data and Normalization
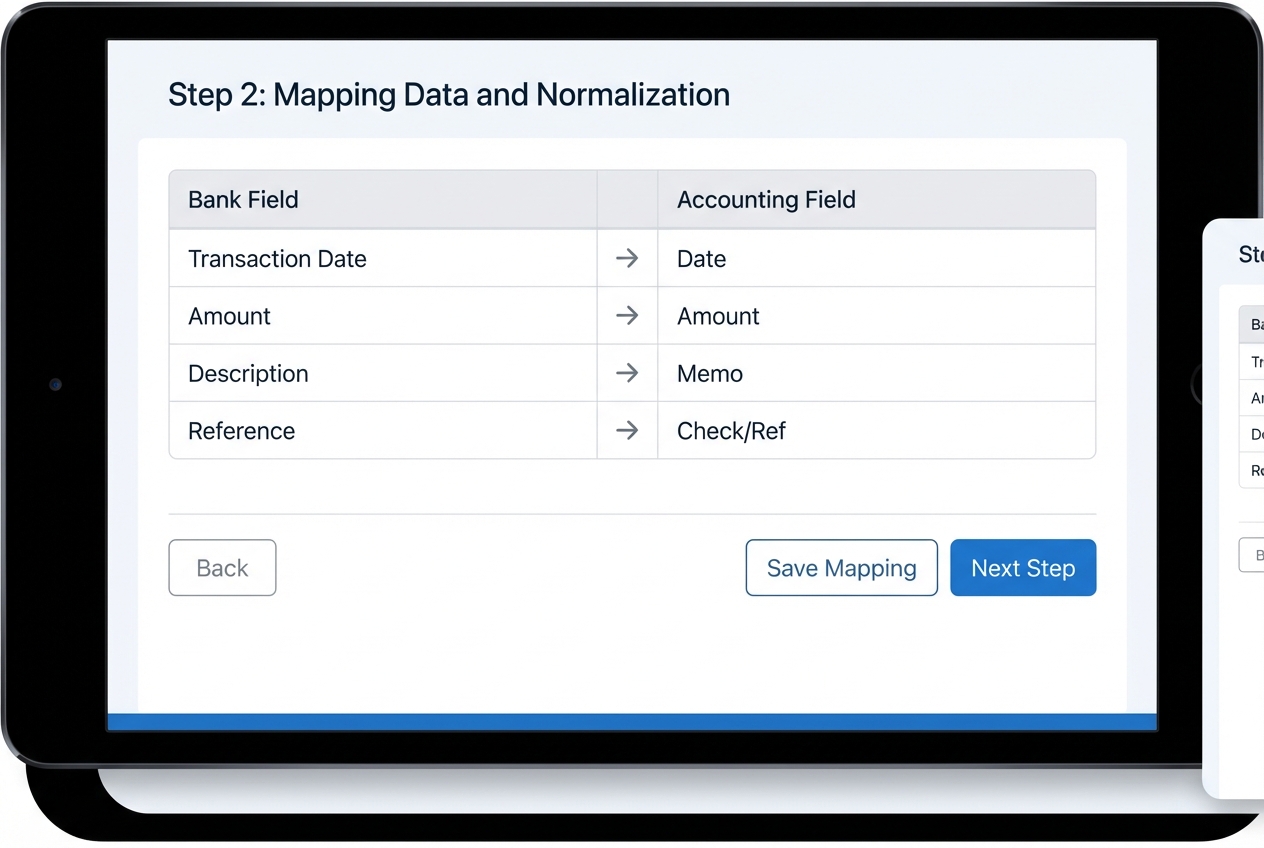
Goal: Make every bank’s data look consistent so matching rules actually work.
Different banks format descriptions, dates, and references differently. Even within the same country, you’ll see variation in:
-
Date formats: Some banks use DD/MM/YYYY, others use MM/DD/YYYY, and that breaks matching fast.
-
Currency codes: You might get “USD” in one feed and “$” in another, which needs standardization.
-
Amount sign conventions: Withdrawals can show as negative values, positive values, or separate debit/credit columns.
-
Merchant descriptors: Vendor names can include noise like locations, terminal IDs, or random strings.
-
Reference IDs: Some transactions have stable references, others have blanks or recycled identifiers.
What to do:
- House standard: Define a canonical format. This is your “house standard.” Set standards for Date and Amount. Do the same for Description, Reference, Currency, and Account ID.
- Field mapping: Map each bank feed field to your accounting field. Keep it explicit. Make it easy to review.
- Description cleanup: Normalize descriptions. Trim extra spaces. Remove random codes that do not help matching.
Practical tip: keep a “mapping change log.” When the bank changes a description format, you’ll want a quick record of what changed and when.
Step 3: Configuring AI-Powered Matching Rules
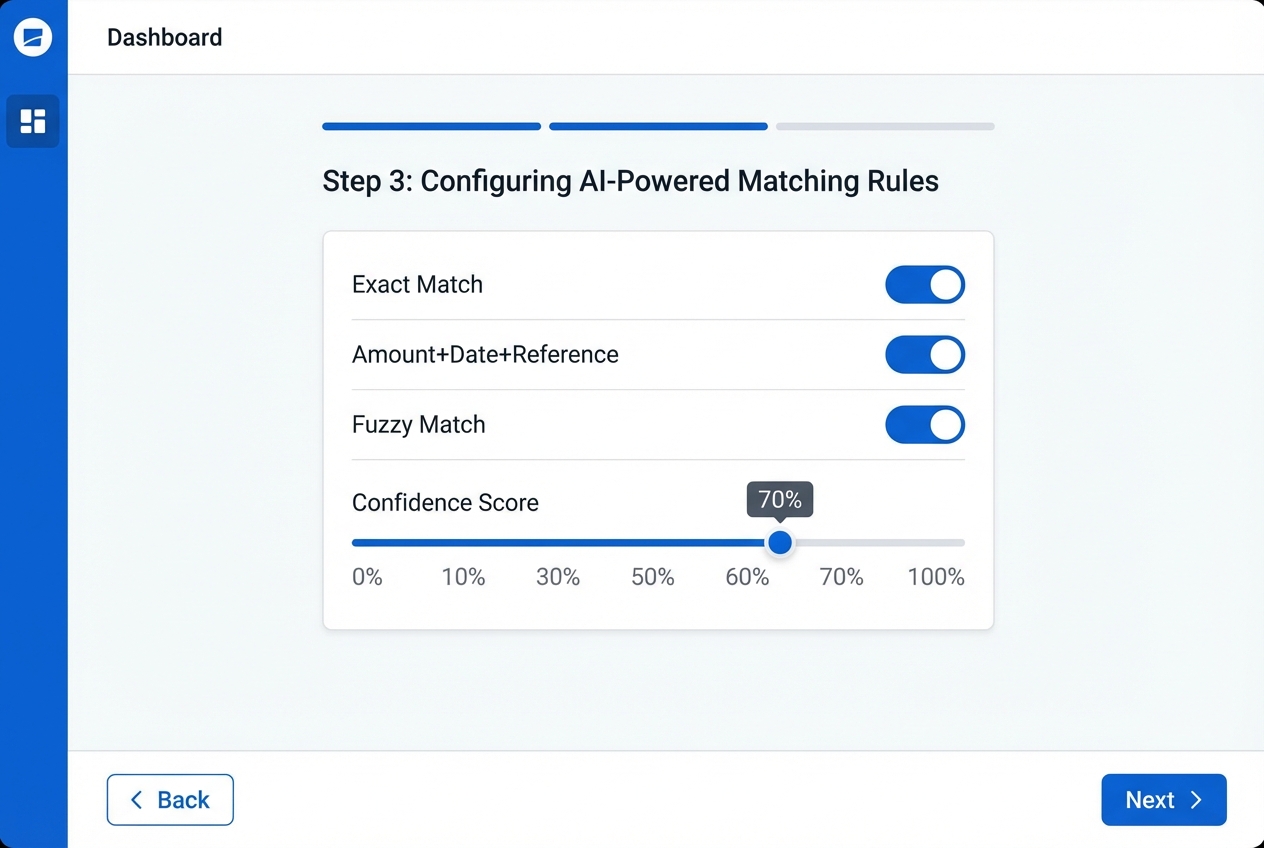
Goal: Automate the matches that are obvious, and handle the messy ones with smart logic.
Start with rules. Then add AI matching where it helps.
Set up two layers:
- Exact match rules: Amount + Date + Reference (or check number).
- Fuzzy logic rules: “Close enough” matching for real life, where one payment may cover multiple invoices, or a payout batch maps to many transactions.
Modern reconciliation platforms use AI-powered matching to handle one-to-many and many-to-one situations with confidence scoring.
What to configure:
-
Exact match keys: Choose stable fields like amount, transaction date, and reference ID to auto-clear clean matches.
-
Tolerance windows: Allow date differences of 1–3 days to handle weekends, processor delays, and bank posting lag.
-
Confidence thresholds: Auto-clear at 95%+ confidence, and route the rest into review so humans stay in control.
-
Grouping rules: Combine related lines like batch deposits, processor payouts, and payroll runs for accurate matching.
Practical tip: Start conservative. Auto-clear only what you are sure about for the first 2–4 weeks. Then expand thresholds once you trust the results.
Step 4: Automated Exception Handling
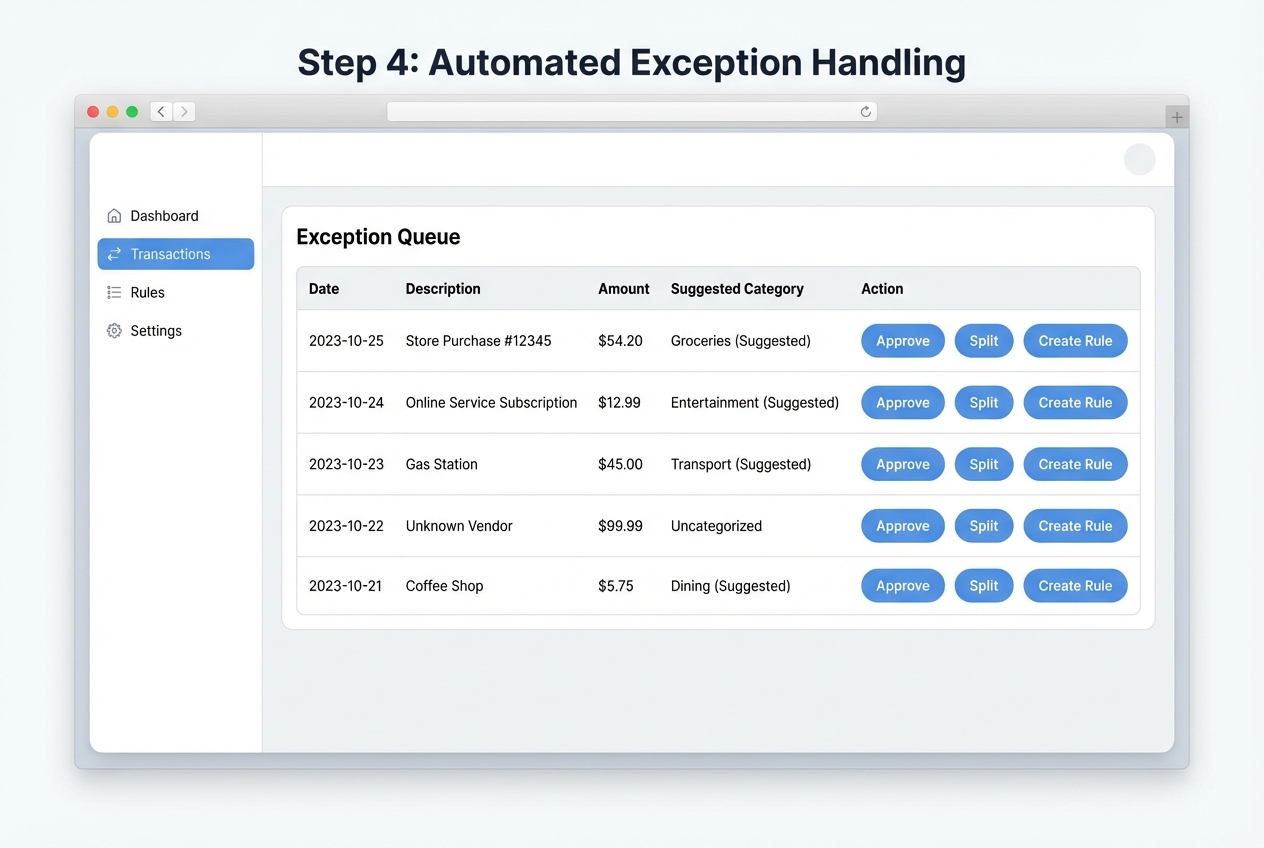
Goal: Make exceptions a workflow, not a firefight.
Even with great rules, you will have exceptions:
-
Bank fees: Small recurring charges that need consistent coding and clearing.
-
FX adjustments: Rounding and exchange differences that cause “almost matched” lines.
-
Wire charges: Fees that show up separately from the wire itself.
-
Chargebacks: Reversals that rarely match cleanly without context.
-
Missing memos: Transactions with blank references or unclear descriptions.
-
Vendor naming surprises: The same vendor showing under multiple names due to processors or subsidiaries.
Your system needs an exception queue that makes review fast and consistent.
What to do:
- Queue setup: Create an “Exception Queue” with clear statuses (New, In Review, Resolved, Rule Created).
- Fast actions: Add one-click actions (Approve, Categorize, Split, Match to Invoice, Create Rule).
- Clear ownership: Assign owners per account. Set a review cadence. Make deadlines visible.
Where QuantumByte can help (when your process is unique): if your exceptions require custom logic, approvals, or multi-system lookups, you can build a lightweight internal tool that fits your workflow exactly. Many business owners start by describing their exception flow in plain language, then turn it into a working app “in days, not months.” You can also extend it with expert developers when edge cases get complex. More on how QuantumByte approaches enterprise workflows.
Step 5: Generating the Reconciliation Report and Audit Trail

Goal: Close the period with confidence and produce auditor-friendly evidence.
Automation is not complete unless it produces a clean, tamper-resistant record of:
-
What matched: Which bank lines tied to which GL entries, including match method (rule, AI, or manual).
-
What didn’t match: Which items stayed open and why they need review.
-
Who approved exceptions: Clear accountability for approvals, recoding, and overrides.
-
What rules were applied: The exact rule version and thresholds used when a match happened.
-
When changes occurred: Time-stamped history so you can answer questions fast during audits.
What to do:
- Period lock: Lock the period so past transactions cannot be quietly edited.
- Summary report: Generate a reconciliation summary. Include beginning balance, cleared items, uncleared items, and ending balance.
- Auditor exports: Export reports for auditors (PDF/CSV). Store them in a controlled location.
- Audit log review: Review the audit log for outliers. Look for unusual manual clears, late changes, or repeated exceptions.
Key Features to Look for in Automation Software
-
Multi-bank integration: This lets you aggregate accounts across institutions (and countries) without juggling portals and exports.
-
ERP compatibility: Look for native sync. If that is not available, demand a strong API. Confirm it connects to your ERP like NetSuite or QuickBooks. If you run a bigger stack, check support for Sage, SAP, and Microsoft Dynamics too.
-
Agentic AI capabilities: Agentic AI means the system can take action, not just suggest. For reconciliation, that can look like investigating a mismatch by pulling an invoice, checking an email receipt, or proposing a coding rule based on past patterns. Custom solutions can be built using Quantum Byte's technology.
-
Customizable thresholds: You need tolerance rules for penny differences, FX rounding, and bank timing delays.
Here’s a quick comparison to help you pick the right lane:
| Option | Best for | Pros | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excel-based matching | Very low volume, temporary stopgap | Cheap, familiar | Breaks at scale, weak audit trail, error-prone |
| Off-the-shelf reconciliation software | Standard workflows, mid to high volume | Faster rollout, proven patterns | Can be rigid if your process is unique |
| Custom automation (RPA + app + integrations) | Unique workflows, many systems, fast scaling | Fits your exact process, can become a competitive advantage | Requires build effort and good requirements |
If you are in the “custom” bucket, QuantumByte can be a strong fit because you can start with an AI-built internal tool and then extend it with the in-house team when you hit edge cases. That is often the difference between “we tried automation” and “we actually own a system that scales.”
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
-
Inconsistent data quality: Use automation (including RPA-style preprocessing) to clean descriptions before matching. M merchant names where possible. Keep raw data stored too, so you can trace back to the source.
-
Handling bank fees: Create auto-posting rules for recurring charges. For example, “Monthly account fee” can automatically post to Bank Fees and clear itself. Review the rule monthly until you trust it.
-
Resistance to change: Show the “time-back” value. Start with one bank account and one month. Let the team feel the relief. Then expand. Also, keep humans in control for approvals early on, so trust builds naturally.
Conclusion
Bank reconciliation automation is no longer an optional luxury. It is a competitive requirement when your transaction volume grows and your time matters. The payoff is simple: less manual work, fewer errors, faster detection of problems, and clean cash visibility you can trust.
If you want to move from reactive cleanup to proactive financial oversight, start with direct feeds, strong data normalization, and clear exception workflows. Then layer in AI matching once the foundation is solid.
When you’re ready to build an automation roadmap that fits your business (not a generic template), QuantumByte can help you scope and ship it quickly. You can start by outlining your workflow and turning it into a working system inside QuantumByte’s app builder, then extend it with expert developers if needed.
Next step: Explore QuantumByte packets and get moving.
FAQs
Can bank reconciliation be automated?
Yes. You automate reconciliation by connecting bank feeds directly to your accounting system (or reconciliation layer) and applying matching rules and algorithms to pair transactions automatically. Exceptions then flow to a review queue.
What is the best automated bank reconciliation software?
It depends on your ERP and complexity. Well-known options include HighRadius and BlackLine. If you have a non-standard workflow or multiple systems that do not “talk” to each other, a custom RPA + integration build can be the best path. QuantumByte can build that kind of workflow-specific system when off-the-shelf tools fall short.
How do you automate a bank reconciliation in Excel?
You can import bank data with Power Query and match against your ledger using lookup formulas (VLOOKUP or INDEX/MATCH) plus some cleanup steps. It can work for small volumes, but it is less secure and less scalable than dedicated automation, especially when you need approvals and audit logs.
What are the main benefits of bank reconciliation automation?
The biggest benefits are major time savings, fewer errors, faster fraud detection, and real-time visibility into cash. The practical win is that your month-end close becomes calmer and more predictable.
Does bank reconciliation software integrate with my current ERP?
Most modern tools do, either through native integrations or APIs. Before you buy, confirm:
-
Sync direction: Check whether the integration is one-way or two-way, and which system is treated as the source of truth.
-
Journal entry handling: Verify how it creates, posts, and reverses entries, especially for fees and FX differences.
-
Audit logging: Ensure every change and manual action is logged with timestamps and user attribution.
